
You can try it for 14 days completely free of charge for evaluation purposes. It helps you code fast with Code Completion and customizable Code Snippets by getting suggestions for keywords and stripping the repetition from coding. Example SQL statements were written in Navicat Premium. In today's blog we learned how the SQL CASE Statement can be employed to choose a value based on the underlying data. For example, we could use it to add a target audience column based on the film rating:

The 2nd CASE syntax is ideal for testing discrete values against two or more conditions. Here is the complete CASE statement and query for MySQL: Since the statements are generic in nature, you may have to modify it slightly to suit your particular database type. This example uses the Chinook database with PostgreSQL 11. You can use the Tab key to move from one to the next. CASE WHEN is a SQL function that works a lot like IF THEN in other programming languages. In fact, you'll find the CASE statement at the top of the Flow Control list:Īfter you place the code snippet into the editor, editable sections are color coded to help identify them. Although you can create your own, Navicat comes with many standard SQL statements, including DDL and flow control statements. To help with the CASE statement, Navicat provides Code Snippets that you can simply drag & and drop into the SQL editor. We'll add a column that splits rental prices into three categories: "discount", "regular", and "premium". Here's a query that selects a list of movie titles, along with their release year and rental price: It's also compatible with many cloud databases like Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Amazon Redshift, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, Google Cloud and MongoDB Atlas. It's a powerful database development and administration tool that can simultaneously connect to most popular databases, including MySQL, MariaDB, MongoDB, SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and SQLite databases. To try out the CASE statement, we'll be writing some queries against the Sakila Sample Database using Navicat Premium. If no comparison is true, the result after ELSE is returned, or NULL if there is no ELSE part: If stinationhost is NULL, the row will always show up as typeB, because NULL NULL is not TRUE in SQL. The second CASE syntax returns the result for the first value=compare_value comparison that is true. WITH subquery AS (.) SELECT CASE WHEN EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM subquery WHERE subquery.host stinationhost) THEN 'typeA' ELSE 'typeB' END FROM tableb With queries like that, you have to take care of NULL values. If no condition is true, the result after ELSE is returned, or NULL if there is no ELSE part: The CASE statement comes in two flavors: the first evaluates one or more conditions and returns the result for the first condition that is true. As we'll see in today's blog, it can be used to test for conditions as well as discrete values. So, once a condition is true, it will short circuit, thereby ignoring later clauses, and return the result.
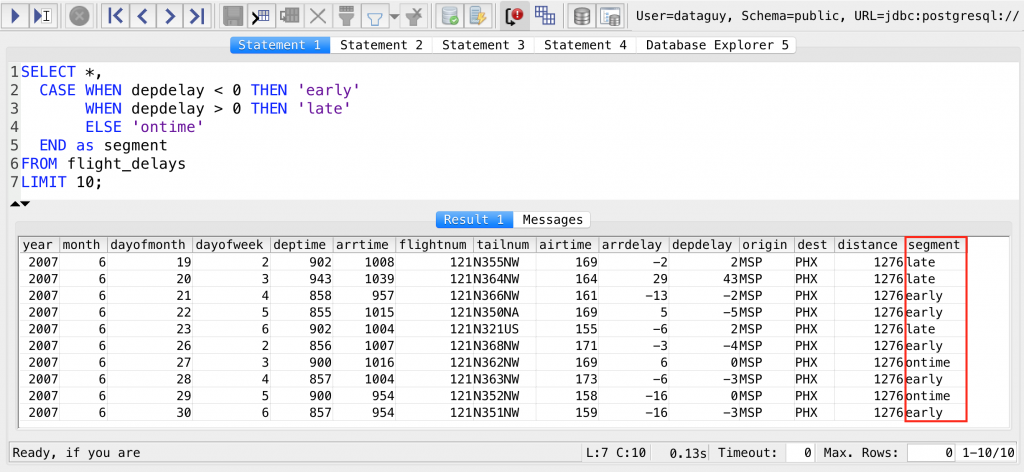
The CASE statement goes through conditions and returns a value when the first condition is met. Third: if the data to be compared is a number, the segment name cannot be written after the case.CASE is a Control Flow statement that acts a lot like an IF-THEN-ELSE statement to choose a value based on the data. Second: in order to use case in the order by block, the query statement needs to repeat the case block in the select block in the order by block It can be clearly seen from the above two examples:įirst: in order to use case in the group by block, the query statement needs to repeat the case block in the select block in the group by block Else 'is greater than 3 and less than 8' endĮlse 'is greater than 3 and less than 8' end DESC


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
